Note: Professor von Hippel has retired from teaching, but continues to run a fully active and funded research program. Applications from potential postdoctoral fellows and undergraduate research participants are welcome.
B.S., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1952. Ph.D., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1955 (D. F. Waugh). Postdoctoral: Naval Medical Research Institute, Bethesda, Maryland, 1956 (M. F. Morales). Honors and Awards: NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, 1952-55; Public Health Service Senior Research Fellow (Career Development Award) 1959-67; John S. Guggenheim Memorial Foundation Fellow, 1973-74; Elected Member, National Academy of Sciences, 1978; Elected Fellow, American Academy of Arts and Sciences, 1979; Merck Award, American Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2002; Elected Member, American Philosophical Society, 2004; Editor, Journal Molecular Biology, 1986-94; Editorial Board, Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1986 - present; Member, Advisory Committee to the Director, NIH, 1987 - 92; American Cancer Society Research Professor of Chemistry, 1989 - present. At Oregon since 1967.
My associates and I are using physical biochemical approaches to study what might be called the molecular basis of gene expression. Most of our experimental work is concerned with the function and regulation of the complexes that control DNA transcription and replication, with studies focused primarily on transcription with the E. coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and its regulatory factors and on replication with the seven-protein bacteriophage T4-coded DNA replication system. Comparative studies are also underway using selected components of some equivalent eukaryotic systems.
In transcription our group is studying the transcription cycle, both at the overall operon level and at the level of the various steps of the single-nucleotide addition-excision cycle. At the operon level we are studying regulatory interactions that control activation and repression at initiation, the kinetics of elongation, and the molecular bases of the elongation-termination decision at both intrinsic and rho-dependent transcription terminators, together with the mechanisms of action antitermination factors. We have recently completed a study of E. coli transcription termination factor rho, in terms of its function as a specific RNA-DNA helicase and as a transcript terminator. Our antitermination studies have focussed on the mechanisms of action of the N protein of phage lambda in N-dependent antitermination systems. At the single-nucleotide addition-excision cycle level we are using various kinetic techniques to understand the molecular origins of transcriptional processivity and fidelity.
In replication our work began with studies of the cooperative binding of the T4 gene 32 (single-stranded DNA binding) protein to the single-stranded DNA (and RNA). This then led us to examine the interactions of the other components of the system, including those of the DNA polymerase with the primer-template and the polymerase accessory proteins. These studies have shown that the basically nonprocessive T4 DNA polymerase can be rendered fully processive by means of "sliding-clamp" processivity factor, and that the role of the other accessory proteins is to carry out the specific and ATP-dependent loading of the processivity factor onto the polymerase at the primer-template junction in the replication fork. The resulting complex can carry out leading strand DNA replication with essentially in vivo rate, fidelity, and processivity. The helicase of the T4 DNA replication system functions as a hexamer and, in combination with a single T4 primase subunit, forms a stable primosome subassembly. We have recently also shown a direct coupling between the polymerase and the helicase. This complex alone, if properly loaded onto a model replication fork, can carry out processive synthesis on a double-stranded DNA construct at the physiological rate. The mode of assembly of these components into a fully functional and coupled DNA replication system is currently being studied.
In all these studies we emphasize the elucidation of the detailed mechanisms and general principles of protein-nucleic acid and protein-protein interactions that underlie the function of these biologically central complexes.
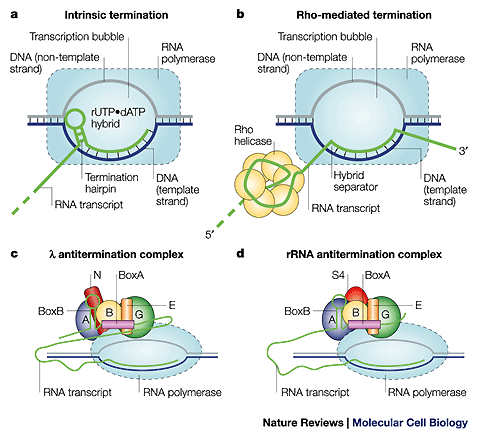
Termination and antitermination complexes that are being studied in the von Hippel laboratory.
Greive S.J. and P.H. von Hippel. (2005) Thinking quantitatively about transcriptional regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:221-32.
Johnson N.P., W.A. Baase, and P.H. Von Hippel (2004) Low-energy circular dichroism of 2-aminopurine dinucleotide as a probe of local conformation of DNA and RNA. PNAS 101:3426-31.
Delagoutte E. and P.H. von Hippel (2003) Function and assembly of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication complex: interactions of the T4 polymerase with various model DNA constructs. J Biol Chem 278:25435-47.
Pasman, Z. and P.H. von Hippel (2002) Active Escherichia coli transcription elongation complexes are functionally homogeneous. J Mol Biol 322:505-19.
Pietroni, P., M.C. Young, G.J. Latham, and P.H. von Hippel (2001) Dissections of the ATP-driven reaction cycle of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication processivity clamp loading system. J Mol Biol 309:869-91.
von Hippel, P.H. and E. Delagoutte (2001) A general model for nucleic acid helicases and their "coupling" within macromolecular machines. Cell 104:177-90.
1. von Hippel, P.H. and D.F. Waugh. Casein: monomers and polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 4311-4319 (1955).
2. Waugh, D.F. and P.H. von Hippel. k-casein and the stabilization of casein micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78, 4576-4582 (1956).
3. von Hippel, P.H., Gellert, M.F. and M.F. Morales. Some physical and enzymatic phenomena in solutions of myosin B. Proc. Conf. on the Chemistry of Muscle Contraction, Tokyo, Japan, 1-14 (1957).
4. Waugh, D.F., von Hippel, P.H. and E.S. Kleiner. The mechanism of the coagulation of milk by rennin. Biophys. Soc. Meeting, Abstr. G8, Cambridge, Massachusetts (1958).
5. von Hippel, P.H., Schachman, H.K., Appel, P. and M.F. Morales. On the molecular weight of myosin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 28, 504-507 (1958).
6. Gellert, M.F., von Hippel, P.H., Schachman, H.K. and M.F. Morales. Studies on the contractile proteins of muscle: I. The ATP-myosin B interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 81, 1384-1393 (1959).
7. von Hippel, P.H., Gellert, M.F. and M.F. Morales. Studies on the contractile proteins of muscle: II. Polymerization reactions in the myosin B system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 81, 1393-1400 (1959).
8. Harrington, W.F., von Hippel, P.H. and E. Mihalyi. Proteolytic enzymes as probes of the secondary structure of fibrous proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 32, 303-304 (1959).
9. Seifter, S., Gallop, P.M., Harrington, W.F., von Hippel, P.H., Michaels, S. and E. Meilman. The specificity of collagenase. Biophys. Soc. Meeting, Abstr. D8, New York (1959).
10. von Hippel, P.H. and W.F. Harrington. Enzymatic studies on the gelatin -> collagen-fold transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 36, 427-447 (1959).
11. von Hippel, P.H., Gallop, P.M., Seifter, S. and R.S. Cunningham. An enzymatic examination of the structure of the collagen macromolecule. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82, 2774-2786 (1960).
12. von Hippel, P.H. and W.F. Harrington. The structure and stabilization of the collagen macromolecule. In "Protein Structure and Function", Brookhaven Symp. Biol. 13, 213-231 (1960).
13. Harrington, W.F. and P.H. von Hippel. Formation and stabilization of the collagen-fold. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 92, 100-113 (1961).
14. Harrington, W.F. and P.H. von Hippel. The structure of collagen and gelatin. Adv. Prot. Chem. 16, 1-138 (1961).
15. Felsenfeld, G. and P.H. von Hippel. Optical melting-point dispersion of DNA. Abstr. Biophys. Soc. Meeting, Washington, D.C. (1962).
16. von Hippel, P.H. and K.-Y. Wong. The effect of ions on the kinetics of formation and the stability of the collagen-fold. Biochemistry 1, 664-674 (1962).
17. Englander, S.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Tritium-exchange in the study of protein structure, with particular reference to the collagen-gelatin system. Symposium on Protein Interactions and Structure. Am. Chem. Soc. Meeting Abstr., Atlantic City, New Jersey (1962).
18. von Hippel, P.H. and K.-Y. Wong. The collagen-> gelatin phase transition. I. Further studies on the effects of solvent environment and polypeptide chain composition. Biochemistry 2, 1387-1398 (1963).
19. von Hippel, P.H. and K.-Y. Wong. The collagen-> gelatin phase transition. II. Shape of the melting curves and effect of chain length. Biochemistry 2, 1399-1413 (1963).
20. Felsenfeld, G., Sandeen, G. and P.H. von Hippel. The destabilizing effect of ribonuclease on the helical DNA structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 50, 644-651 (1963).
21. von Hippel, P.H. and G. Felsenfeld. Micrococcal nuclease as a probe of DNA conformation. Biochemistry 3, 27-39 (1964).
22. von Hippel, P.H. and K.-Y. Wong. Neutral salts: The generality of their effects on the stability of macromolecular conformations. Science 145, 577-580 (1964).
23. Printz, M.P. and P.H. von Hippel. Hydrogen exchange studies of DNA structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 53, 363-370 (1965).
24. von Hippel, P.H. and K.-Y. Wong. On the conformational stability of globular proteins: The effects of various electrolytes and nonelectrolytes on the thermal ribonuclease transition. J. Biol. Chem. 240, 3909-3923 (1965).
25. von Hippel, P.H. and M.P. Printz. Dynamic aspects of DNA structure as studied by hydrogen exchange. Fed. Proc. 24, 1458-1465 (1965).
26. von Hippel, P.H. Collagens. In "The Encyclopedia of Biochemistry," R.J. Williams and E.M. Lansford, Jr., eds., Reinhold, New York, pp. 259-260 (1967).
27. Olins, D.E., Olins, A.L. and P.H. von Hippel. Model nucleoprotein complexes: Studies on the interaction of cationic homopolypeptides with DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 24, 157-176 (1967).
28. von Hippel, P.H. Structure and stabilization of the collagen molecule in solution. In "Treatise on Collagen," Vol. I, G.N. Ramachandran, ed., Academic Press, London, pp. 253-338 (1967).
29. Olins, D.E., Olins, A.L. and P.H. von Hippel. On the structure and stability of DNA-protamine and DNA-polypeptide complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 33, 265-281 (1968).
30. Wingert, L. and P.H. von Hippel. The conformation dependent hydrolysis of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 157, 114-126 (1968).
31. Lees, C.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Hydrogen-exchange studies of deoxyribonucleic acid-protein complexes. Development of a filtration method and application to the deoxyribonucleic acid-polylysine system. Biochemistry 7, 2480-2488 (1968).
32. Printz, M.P. and P.H. von Hippel. On the kinetics of hydrogen exchange in deoxyribonucleic acid. pH and salt effects. Biochemistry 7, 3194-3206 (1968).
33. Schleich, T.W., Gentzler, R. and P.H. von Hippel. Proton exchange of N-methylacetamide in concentrated aqueous electrolyte solutions: I. Acid catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90, 5954-5960 (1968).
34. von Hippel, P.H. and T.W. Schleich. Ion effects on the solution structure of biological macromolecules. Accts. Chem. Res. 2, 257-265 (1969).
35. von Hippel, P.H. and T.W. Schleich. The effects of neutral salts on the structure and conformational stability of macromolecules in solution. In "Biological Macromolecules," Vol. II, G.D. Fasman and S.N. Timasheff, eds., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 417-584 (1969).
36. Schleich, T.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Specific ion effects on the solution conformation of poly-L-proline. Biopolymers 7, 861-877 (1969).
37. von Hippel, P.H. Conformational aspects of the nucleic acid-protein recognition problems. J. Cell Physiol. 74 (Suppl. 1), 235-238 (1969).
38. McConnell, B.M. and P.H. von Hippel. Hydrogen exchange as a probe of the dynamic structure of DNA. I. General acid-base catalysis. J. Mol. Biol. 50, 297-316 (1970).
39. McConnell, B.M. and P.H. von Hippel. Hydrogen exchange as a probe of the dynamic structure of DNA. II. Effects of base composition and destabilizing salts. J. Mol. Biol. 50, 317-332 (1970).
40. Schleich, T.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Ion-induced water-proton chemical shifts and the conformational stability of macromolecules. Biochemistry 9, 1059-1066 (1970).
41. McConnell, B.M. and P.H. von Hippel. Hydrogen exchange measurements on nucleic acids. In "Procedures in Nucleic Acid Research", Vol. II, G.L. Cantoni and D.R. Davies, eds., Harper and Row, New York and London, pp. 389-406 (1971).
42. von Hippel, P.H. and K.-Y. Wong. Dynamic aspects of native DNA structure: Kinetics of the formaldehyde reaction with calf thymus DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 61, 587-613 (1971).
43. Schleich, T.W., Rollefson, B. and P.H. von Hippel. Proton exchange of N-methylacetamide in concentrated aqueous electrolyte solutions. II. Acid catalysis in water-dioxane mixtures and base catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 93, 7070-7074 (1971).
44. Englander, J.J. and P.H. von Hippel. Slow exchange of the "outside" amino hydrogens of DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 63, 171-177 (1972).
45. Laiken, S.L., Gross, C.A. and P.H. von Hippel. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of Escherichia coli lac repressor-inducer interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 66, 143-155 (1972).
46. von Hippel, P.H. and J.D. McGhee. DNA-protein interactions. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 41, 231-300 (1972).
47. von Hippel, P.H., Peticolas, V., Schack, L. and L. Karlson. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. I. Ion binding to polyacrylamide and polystyrene columns. Biochemistry 12, 1256-1264 (1973).
48. Hamabata, A. and P.H. von Hippel. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. II. Effects of vicinal hydrophobic groups on the specificity of binding of ions to amide groups. Biochemistry 12, 1264-1271 (1973).
49. Hamabata, A., Chang, S. and P.H. von Hippel. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. III. Solubility of fatty acid amides in ionic solutions. Biochemistry 12, 1271-1278 (1973).
50. Hamabata, A., Chang, S. and P.H. von Hippel. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. IV. Properties of fatty acid amide micelles. Biochemistry 12, 1278-1282 (1973).
51. Melchior, W.B. Jr. and P.H. von Hippel. Alteration of the relative stability of dA•dT and dG•dC base pairs in DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 298-302 (1973).
52. von Hippel, P.H. and A. Hamabata. Model studies on the effects of neutral salts on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. J. Mechanochem. and Cell Motility (Memorial Issue Dedicated to Professor Aharon Katzir-Katchalsky) 2, 127-138 (1973).
53. Yee, R.Y., Englander, S.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Native collagen has a two-bonded structure. J. Mol. Biol. 83, 1-16 (1974).
54. McGhee, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: Cooperative and non-cooperative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J. Mol. Biol. 86, 469-489 (1974).
55. Engel, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Effects of methylation on the stability of nucleic acid conformations: Studies at the monomer level. Biochemistry 13, 4143-4158 (1974).
56. von Hippel, P.H., Revzin, A., Gross, C.A. and A.C. Wang. Non-specific DNA binding of genome regulating proteins as a biological control mechanism. I. The lac operon: Equilibrium aspects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 4808-4812 (1974).
57. von Hippel, P.H., Revzin, A., Gross, C.A. and A.C. Wang. Interaction of lac repressor with non-specific DNA binding sites. In "Protein-ligand interactions." H. Sund and G. Blauer, eds., Walter de Gruyter, Berlin and New York, pp. 270-288 (1975).
58. von Hippel, P.H. Neutral salt effects on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules. In "Protein-Ligand Interactions." H. Sund and G. Blauer, eds., Walter de Gruyter, Berlin and New York, pp. 452-471 (1975).
59. McGhee, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Formaldehyde as a probe of DNA structure. I. Reaction with exocyclic amino groups of DNA bases. Biochemistry 14, 1281-1296 (1975).
60. McGhee, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Formaldehyde as a probe of DNA structure. II. Reaction with endocyclic imino groups of DNA bases. Biochemistry 14, 1297-1303 (1975).
61. von Hippel, P.H. Neutral salt effects on the conformational stability of biological macromolecules: Model studies. Proceedings CNRS Symposium on Participation Energetique de l'eau Solvant aux Interactions Specfiques dans les Systems Biologiques", No. 246, 19-26 (1976).
62. Draper, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Polynucleotide binding properties of E. coli ribosomal protein Sl. In "Molecular Mechanisms in the Control of Gene Expression." D.P. Nierlich, W.J. Rutter and C.F. Fox, eds., ICN-UCLA Symposia on Molecular and Cellular Biology, Volume V, pp. 421-426 (1976).
63. Jensen, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. DNA "melting proteins". I. Effects of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease binding on the conformation and stability of DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7198-7214 (1976).
64. Jensen, D.E., Kelly, R.C. and P.H. von Hippel. DNA "melting" proteins. II. Effects of bacteriophage T4 gene 32-protein binding on the conformation and stability of nucleic acid structures. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7215-7228 (1976).
65. Kelly, R.C. and P.H. von Hippel. DNA "melting" proteins. III. Fluorescence "mapping" of the nucleic acid binding site of bacteriophage T4 gene 32-protein. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7229-7239 (1976).
66. Kelly, R.C., Jensen, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. DNA "melting" proteins. IV. Fluorescence measurements of binding parameters for bacteriophage T4 gene 32-protein to mono-, oligo- and polynucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7240-7250 (1976).
67. von Hippel, P.H., Jensen, D.E., Kelly, R.C. and J.D. McGhee. Molecular approaches to the interaction of nucleic acids with "melting" proteins. In "Nucleic Acid-Protein Recognition," H.J. Vogel, ed., Academic Press, New York, pp. 65-89 (1977).
68. McGhee, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Formaldehyde as a probe of DNA structure: III. Equilibrium denaturation of DNA and synthetic polynucleotides. Biochemistry 16, 3267-3276 (1977).
69. McGhee, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Formaldehyde as a probe of DNA structure: IV. Mechanism of the initial reaction of formaldehyde with DNA. Biochemistry 16, 3276-3293 (1977).
70. Jensen, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. A boundary sedimentation velocity method for determining non-specific nucleic acid-protein interaction binding parameters. Anal. Biochem. 80, 267-281 (1977).
71. Wang, A.C., Revzin, A., Butler, A.P. and P.H. von Hippel. Binding of E. coli lac repressor to non-operator DNA. Nucl. Acid Res. 4, 1579-1592 (1977).
72. Butler, A.P., Revzin, A. and P.H. von Hippel. Molecular parameters characterizing the interaction of lac repressor with inducer and non-operator DNA. Biochemistry 16, 4757-4768 (1977).
73. Revzin, A. and P.H. von Hippel. Direct measurements of association constants for the binding of E. coli lac repressor to non-operator DNA. Biochemistry 16, 4769-4776 (1977).
74. Kao-Huang, Y., Revzin, A., Butler, A.P., O'Connor, P., Noble, D. and P.H. von Hippel. Non-specific DNA binding of genome regulating proteins as a biological control mechanism: measurement of DNA-bound E. coli lac repressor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 4228-4232 (1977).
75. Draper, D.E., Pratt, C.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 has two polynucleotide binding sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 4786-4790 (1977).
76. Engel, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Effects of methylation on the stability of nucleic acid conformations: Studies at the polymer level. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 927-934 (1978).
77. Engel, J.D. and P.H. von Hippel. d(m6ATP) as a probe of the fidelity of base incorporation into polynucleotides by E. coli DNA polymerase I. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 5935-5939 (1978).
78. Draper, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Nucleic acid binding properties of E. coli ribosomal protein S1. I. Structure and interactions of binding site I. J. Mol. Biol. 122, 321-338 (1978).
79. Draper, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Nucleic acid binding properties of E. coli ribosomal protein S1. II. Cooperativity and specificity of binding site II. J. Mol. Biol. 122, 339-359 (1978).
80. von Hippel, P.H. On the molecular bases of the specificity of interaction of transcriptional proteins with genome DNA. In "Biological Regulation and Development," Vol. 1, R.F. Goldberger, ed., Plenum Publishing Corp., New York, pp. 279-347 (1979).
81. von Hippel, P.H. On the interactions of genome-regulatory proteins with DNA. In "FEBS Federation of European Biochemical Societies, 12th Meeting Dresden l978", Volume 51, Gene Functions, S. Rosenthal et al., ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 95-108 (1979).
82. Draper, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Measurement of macromolecular equilibrium binding constants by a sucrose gradient band sedimentation method: Application to protein-nucleic acid interactions. Biochemistry 18, 753-760 (1979).
83. Draper, D.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Interaction of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 with ribosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 1040-1044 (1979).
84. Woodbury, C.P. Jr., Hagenbuchle, O. and P.H. von Hippel. DNA site recognition and reduced specificity of the EcoRI endonuclease. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 11534-11546 (1980).
85. Woodbury, C.P. Jr., Downey, R.L. and P.H. von Hippel. DNA site recognition and overmethylation by the EcoRI methylase. J. Biol. Chem. 225, 11526-11533 (1980).
86. Kowalczykowski, S.C., Lonberg, N., Newport, J.W., Paul, L. and P.H. von Hippel. On the thermodynamics and kinetics of the cooperative binding of bacteriophage T4 coded gene 32 (helix destabilizing) protein to nucleic acid lattices. Biophys. J. 32, 403-418 (1980)
87. Newport, J.W., Kowalczykowski, S.C., Lonberg, N., Paul, L.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Molecular aspects of the interactions of T4-coded gene 32-protein and DNA polymerase (gene 43-protein) with nucleic acids. In "Mechanistic Studies of DNA Replication and Genetic Recombination" (B. Alberts, ed.) ICN-UCLA Symposia on Molecular and Cellular Biology, Volume XIX, pp. 485-505 (1981).
88. Woodbury, C.P. Jr. and P.H. von Hippel. Relaxed sequence specificities of EcoRI endonuclease and methylase: mechanisms, possible practical applications and uses in defining protein-nucleic acid recognition mechanisms. In "The Restriction Endonucleases", Volume I, J. Chirikjian, ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 181-207 (1981).
89. Kowalczykowski, S.C., Lonberg, N., Newport, J.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of T4 coded gene 32-protein with nucleic acids. I. Characterization of the binding interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 145, 475-104 (1981).
90. Newport, J.W., Lonberg, N., Kowalczykowski, S.C. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of T4 coded gene 32-protein with nucleic acids. II. Specificity of binding to DNA and RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 145, 4105-121 (1981).
91. Lonberg, N., Kowalczykowski, S.C., Paul, L.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of T4 coded gene 32-protein with nucleic acids. III. Binding properties of two specific products of the protein (G32P*I and G32P*III). J. Mol. Biol. 145, 123-138 (1981).
92. Kowalczykowski, S.C., Bear, D.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins. In "The Enzymes", Volume 14, P. Boyer, ed., Academic Press, New York, pp. 373-444 (1981).
93. Berg, O.G., Winter, R.B. and P.H. von Hippel. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. I. Models and theory. Biochemistry 20, 6926-6948 (1981).
94. Winter, R.B. and P.H. von Hippel. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. II. The E. coli lac repressor-operator interaction: equilibrium measurements. Biochemistry 20, 6948-6960 (1981).
95. Winter, R.B., Berg, O.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. III. The E. coli lac repressor-operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry 20, 6961-6977 (1981).
96. von Hippel, P.H., Bear, D.G., Winter, R.B. and O.G. Berg. Molecular aspects of promoter function: an overview. In "Promoters: Structure and Function" (R. Rodriguez and M. Chamberlin, eds.), Praeger Scientific Publishing Co., New York, 3-33 (1982).
97. Berg, O.G., Winter, R.B. and P.H. von Hippel. How do genome-regulatory proteins locate their DNA target sites? Trends Biochem. Sci. 7, 52-55 (1982).
97a. Reprinted in "DNA Makes RNA Makes Protein", T. Hunt, S. Prentis and J. Tooze, eds., Elsevier, Amsterdam.
98. von Hippel, P.H., Kowalczykowski, S.C., Lonberg, N., Newport, J.W., Paul, L.S., Stormo, G.D. and L. Gold. Autoregulation of gene expression: Quantitative evaluation of the expression and function of the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 (single-stranded DNA binding) protein system. J. Mol. Biol. 162, 6795-6818 (1982).
99. von Hippel, P.H. and F.R. Fairfield. Quantitative approaches to the autogenous regulation of gene expression. In "Symposium on Mobility and Recognition in Cell Biology". H. Sund and C. Veeger, eds., Walter Gruyter, Berlin and New York, 213-236 (1983).
100. von Hippel, P.H. and D.G. Bear. Location and recognition of specific DNA binding sites by proteins that regulate gene expression. In "Symposium on Mobility and Recognition in Cell Biology". H. Sund and C. Veeger, eds., Walter de Gruyter, Berlin and New York, 291-316 (1983).
101. von Hippel, P.H., Newport, J.W., Paul, L.S., Fairfield, F.R., Hockensmith, J.W. and M.K. Dolejsi. Dynamic and structural interactions in the T4 DNA replication complex. In "Mechanisms of DNA Replication and Recombination". N.R. Cozzarelli, ed., UCLA Symposia on Molecular and Cellular Biology, New Series, Volume 10. Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York pp. 153-171 (1983).
102. Morgan, W.D., Bear, D.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Rho-dependent termination of transcription: I. Identification and characterization of termination sites for transcription from the bacteriophage l PR promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 9553-9564 (1983).
103. Morgan, W.D., Bear, D.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Rho-dependent termination of transcription: II. Kinetics of mRNA elongation during transcription from the bacteriophage g PR promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 9565-9574 (1983).
104. Woodbury, C.P. Jr. and P.H. von Hippel. On the determination of DNA-protein interaction parameters using the nitrocellulose filterbinding assay. Biochemistry 22, 4730-4737 (1983).
105. von Hippel, P.H., Kowalczykowski, S.C., Lonberg, N., Newport, J.W., Paul, L.S., Stormo, G.D. and L. Gold. Autoregulation of expression of T4 gene 32: A quantitative analysis. In "Bacteriophage T4", C. Mathews and B. Kutter, eds., American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., pp. 202-207 (1983).
106. Fairfield, F.R., Newport, J.W., Dolejsi, M.K. and P.H. von Hippel. On the processivity of DNA replication. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1, 715-727 (1983).
107. Morgan, W.D., Bear, D.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Specificity of release by Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho of nascent mRNA transcripts initiated at the g PR promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 8664-8671 (1984).
108. von Hippel, P.H., Bear, D.G., Morgan, W.D. and J.A. McSwiggen. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: A molecular analysis. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 53, 389-446 (1984).
109. Berg, O.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 14, 131-160 (1985).
110. von Hippel, P.H. and F.R. Fairfield. Thermodynamic aspects of the regulation of protein synthesis in bacteria. Pure Applied Chem. 57, 45-56 (1985).
111. Bear, D.G., Andrews, C.L., Singer, J.D., Morgan, W.D., Grant, R.A., von Hippel, P.H. and T. Platt. E. coli transcription termination factor rho has a two domain structure in its activated form. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 1911-1915 (1985).
112. Morgan, W.D., Bear, D.G., Litchman, B.L. and P.H. von Hippel. mRNA sequence and secondary structure requirements for rho-dependent transcription termination. Nucl. Acids Res. 13, 3739-3754 (1985).
113. von Hippel, P.H. Close encounters of nucleic acids and proteins. Cell 42, 407-410 (1985).
114. Bear, D.G., McSwiggen, J.A., Morgan, W.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Mechanisms of rho-dependent transcription termination site selection. In Proceedings of the UCLA Symposium on "Sequence Specificity in Transcription and Translation", R. Calendar and L. Gold, eds., Alan R. Liss, Publishers, pp. 137-150 (1985).
115. Kowalczykowski, S.C., Paul, L.S., Lonberg, N., Newport, J.W. and P.H. von Hippel. The cooperative and noncooperative binding of protein ligands to nucleic acid lattices: Experimental approaches to the determination of thermodynamic parameters. Biochemistry 25, 1226-1240 (1986).
116. Hockensmith, J.W., Kubasek, W.L., Vorachek, W.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Laser crosslinking of nucleic acids to proteins: Methodology and first applications to the phage T4 DNA replication system. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 3512-3518 (1986).
117. von Hippel, P.H. and O.G. Berg. On the specificity of DNA-protein interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 1608-1612 (1986).
118. Berg, O.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. I. Statistical-mechanical theory and application to operators and promoters. J. Mol. Biol. 193, 723-750 (1987).
119. von Hippel, P.H. and O.G. Berg. On the nature of specificity of DNA protein interactions in the regulation of gene expression. In NATO Advanced Study Institute Proceedings on "DNA-Ligand Interactions: From Drugs to Proteins", W. Guschlbauer, ed., pp. 159-171 (1987).
120. von Hippel, P.H., Yager, T.D., Bear, D.G., McSwiggen, J.A., Geiselmann, J., Gill, S.C., Linn, J.D. and W.D. Morgan. Mechanistic aspects of transcript elongation and rho-dependent termination in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the 16th Steenbock Symposium (held in July 1986) on "RNA Polymerase and the Regulation of Transcription", W. Reznikoff et al., eds., Elsevier, pp. 325-334 (1987).
121. Hockensmith, J.W., Kubasek, W.L., Cross, T.A., Dolejsi, M.K., Vorachek, W.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Dynamic and static structural studies of the bacteriophage T4-coded DNA replication complex, using UV laser crosslinking. In "DNA Replication and Recombination". UCLA Symposium on Molecular and Cellular Biology, New Series, on "Mechanisms of DNA Replication", T. Kelly and R. McMaken, eds., Alan R. Liss, NY, pp. 111-123 (1987).
122. Yager, T.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Transcript elongation and termination in E. coli. In "Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology", F. Neidhardt et al., eds., American Society of Microbiology, pp. 1241-1275 (1987).
123. Berg, O.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. II. The binding of cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP) to regulatory sites. J. Mol. Biol. 200, 709-723 (1988).
124. McSwiggen, J.A., Bear, D.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho with RNA. I. Binding stoichiometries and free energies. J. Mol. Biol. 199, 609-622 (1988).
125. Bear, D.G., Hicks, P.S., Escudero, K.W., Andrews, C.L., McSwiggen, J.A. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of E. coli transcription termination factor rho with RNA. II. Electron microscopy and nuclease protection experiments. J. Mol. Biol. 199, 623-635 (1988).
126. Berg, O.G. and P.H. von Hippel. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 13, 207-211 (1988).
127. Seifried, S.E., Wang, Y. and P.H. von Hippel. Fluorescent modification of the cysteine-202 residue of E. coli transcription termination factor rho. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 13511-13514 (1988).
128. von Hippel, P.H. and O.G. Berg. DNA-protein interaction in the regulation of gene expression. In "Topics in Structural and Molecular Biology: Protein-Nucleic Acid Interaction", W. Saenger and U. Heinemann, eds. The Macmillan Press, Ltd., London, England, pp. 1-18 (1989).
129. von Hippel, P.H. and O.G. Berg. Facilitated target location in biological systems. (Minireview) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 675-678 (1989).
130. Kubasek, W.L., Hockensmith, J.W., Voracek, W., Spann, D., Munck, K.T., Evertsz, E. and P.H. von Hippel. UV laser crosslinking of proteins with nucleic acids. Ber der Bunsen - Gesellschaft fur Physkialische Chemie 93, 406-410 (1989).
131. Jarvis, T.C., Paul, L.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Structural and enzymatic studies of the T4 DNA replication system: I. Physical characterization of the polymerase accessory proteins complex. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 12709-12716 (1989).
132. Jarvis, T.C., Paul, L.S., Hockensmith, J.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Structural and enzymatic studies of the T4 DNA replication system: II. ATPase properties of the polymerase accessory proteins complex. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 12717-12729 (1989).
133. Gill, S.C. and P.H. von Hippel. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Analytical Biochem. 182, 319-326 (1989).
134. Jarvis, T.E., Dolejsi, M.K., Hockensmith, J.W., Kubasek, W.L., Paul, L.S., Reddy, M.K. and P.H. von Hippel. Structural and functional analysis of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication complex. Proc. UCLA Symposium, "Molecular Mechanisms in DNA Replication and Recombination," C. Richardson and R. Lehman, eds., Alan Liss Publishers, New York, pp. 261-275 (1990).
135. Jarvis, T.C., Ring, D.M., Daube, S.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Macromolecular crowding: Thermodynamic consequences for protein-protein interactions in the T4 DNA replication complex. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 15160-15167, (1990).
136. Gill, S.C., Yager, T.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Thermodynamic analysis of the transcription cycle in E. coli. Biophys. Chem. 37, 239-250 (1990).
137. Jarvis, T.C., Newport, J.W. and P.H. von Hippel. Stimulation of the processivity of the DNA polymerase of bacteriophage T4 by the polymerase accessory proteins: The role of ATP hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem., 266, 1830-1840 (1991).
138. von Hippel, P.H. Preface, In "The Biology of Non-Specific DNA-Protein Interaction." A. Revzin, ed., CRC Press (1991).
139. Yager, T.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Thermodynamic analysis of RNA transcript elongation and termination in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry, 30, 1097-1118 (1991).
140. Gill, S.C., Weitzel, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel. E. coli sigma70 and NusA proteins. I. Binding interactions with core RNA polymerase in solution and within the transcription complex. J. Mol. Biol., 220, 307-324 (1991).
141. Gill, S.C., Yager, T.D. and P.H. von Hippel. E. coli sigma70 and NusA proteins. II. Physical properties and self-association states. J. Mol. Biol., 220, 325-333 (1991).
142. von Hippel, P.H. and T.D. Yager. Transcript elongation and termination are competitive kinetic processes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 2307-2311 (1991).
143. Hockensmith, J.W., Kubasek, W.L., Vorachek, W.R., Evertsz, E.M. and P.H. von Hippel. Laser cross-linking of protein-nucleic acid complexes. Methods in Enzymology, (R. Sauer, ed.), Academic Press, 208, 211-236 (1991).
144. Gogol, E.P., Seifried, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Structure and Assembly of the E. coli Transcription Termination Factor Rho and its Interactions with RNA: I. Cryoelectron Microscopic Studies. J. Mol. Biol. 221, 1127-1138 (1991).
145. Seifried, S.E., Bjornson, K.P. and P.H. von Hippel. Structure and assembly of the E. coli transcription termination factor Rho and its interactions with RNA: II. Physical chemical studies. J. Mol. Biol. 221, 1139-1151 (1991).
146. Geiselmann, J., Yager, T.D., Gill, S.C., Calmettes, P. and P.H. von Hippel. Physical properties of the E. coli transcription termination factor Rho. I. Association states and geometry of the Rho oligomer. Biochemistry, 31, 111-121 (1992).
147. Geiselmann, J., Seifried, S.E., Yager, T.D., Liang, C. and P.H. von Hippel. Physical properties of the E. coli transcription termination factor Rho. II. Quaternary structure of the Rho hexamer. Biochemistry, 31, 121-132 (1992).
148. von Hippel, P.H. and T.D. Yager. Elongation-termination decision in transcription. Science, 255, 809-812 (1992).
149. Erie, D., Yager, T.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Single nucleotide addition cycle in transcription. Ann. Rev. Biophys. & Biophys. Chem., 21, 379-415 (1992).
150. Gogol, E.P., Young, M.C., Kubasek, W.L., Jarvis, T.C. and P.H. von Hippel. Cryoelectron microscopic visualization of functional sub-assemblies of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication complex. J. Mol. Biol., 224, 395-412 (1992).
151. Reddy, M.K., Weitzel, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Processive Proofreading is Intrinsic to T4 DNA Polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14157-14166 (1992).
152. Geiselmann, J. and P.H. von Hippel. Functional interactions of ligand cofactors with E. coli transcription termination factor Rho: I. Binding of ATP. Protein Sci. 1, 850-860 (1992).
153. Geiselmann, J., Yager, T.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Functional interactions of ligand cofactors with E. coli transcription termination factor Rho: II. Binding of RNA. Protein Sci. 1, 861-873 (1992).
154. von Hippel, P.H., Yager, T.D. and S.C. Gill. Quantitative aspects of the transcription cycle in E. coli. In "Transcription Regulation," S. McKnight and K. Yamamoto, eds., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories, pp. 179-201 (1992).
155. Young, M.C., Reddy, M.K. and P.H. von Hippel. Structure and Function of the Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase Holoenzyme. Biochemistry 31, 8675-8690 (1992).
156. Seifried, S.E., Easton, J.B. and P.H. von Hippel. ATPase activity of transcription termination factor Rho: the functional dimer model. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10454-10458 (1992).
157. Daube, S.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Functional transcription elongation complexes from synthetic RNA-DNA bubble duplexes. Science 258, 1320-1324 (1992).
158. Rees, W.A., Yager, T.D., Korte, J. and P.H. von Hippel. Betaine can eliminate the base pair composition dependence of DNA melting. Biochemistry 32, 137-144 (1993).
159. Wang, Y. and P.H. von Hippel. E. coli transcription termination factor rho. I. ATPase activation by oligonucleotide cofactors. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 13940-13946 (1993).
160. Wang, Y. and P.H. von Hippel. E. coli transcription termination factor rho. II. Binding of oligonucleotide cofactors. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 13947-13955 (1993).
161. Hockensmith, J.W., Kubasek, W.L., Vorachek, W.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Laser crosslinking of proteins to nucleic acids: I. Examining physical parameters of protein-nucleic acid complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 15712-15720 (1993).
162. Hockensmith, J.W., Kubasek, W.L., Evertsz, E.M., Mesner, L.D. and P.H. von Hippel. Laser crosslinking of proteins to nucleic acids: II. Interactions of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication polymerase accessory proteins complex with DNA. J. Biol. Chem., 268, 15721-15730 (1993).
163. Reddy, M.K., Weitzel, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Assembly of a functional replication complex without ATP hydrolysis: A direct interaction of bacteriophage T4 gp45 with T4 DNA polymerase. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 3211-3215 (1993).
164. Geiselmann, J., Wang, Y., Seifried, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel. A physical model for the translocation and helicase activities of E. coli transcription termination protein rho. Proc Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 7754-7778 (1993).
165. Erie, D.A., Hajiseyedjavadi, O., Young, M.C. and P.H. von Hippel. Multiple RNA polymerase conformations and GreA control the fidelity of transcription. Science, 262, 867-873 (1993).
166. Jensen, O.N., Barofsky, D.F., Young, M.C., von Hippel, P.H., Swenson, S. and S.E. Seifried. Direct observation of UV-crosslinked protein-nucleic acid complexes by MALDI mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 7, 496-501 (1993).
167. Anfinsen, C.B., Bessman, M.J., Schachman, H.K., Schellman, J.A., von Hippel, P.H. and M. Young. Remembering Bill Harrington. Trends Biochem. Sci., 18, 364-365 (1993).
168. Jensen, O.N., Barofsky, D.F., Young, M.C., von Hippel, P.H., Swenson, S. and S.E. Seifried. Mass spectrometric protocol for the analysis of UV-crosslinked protein-nucleic acid complexes. Techniques in Protein Chem. V. J.W. Crabb, ed., Academic Press pp. 27-37 (1994).
169. Young, M.C., Reddy, M.K., Jarvis, T.C., Gogol, E.P., Dolejsi, M.K. and P. H.
von Hippel. Protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions in the T4 DNA polymerase accessory protein complex, in "The Molecular Biology of Bacteriophage T4" (J.D. Karam, Editor-in-Chief), American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp. 313-317 (1994).
170. Young, M.C., Kuhl, S.B. and P.H. von Hippel. Kinetic Theory of ATP-driven translocases on one-dimensional polymer lattices. J. Mol. Biol., 235, 1436-1446 (1994).
171. Young, M.C., Schultz, D., Ring, D. and P.H. von Hippel. Bacteriophage T4 gene 41 protein helicase translocates unidirectionally on single-stranded DNA: Kinetic parameters of the reaction. J. Mol. Biol., 235, 1447-1458 (1994).
172. Daube, S.S. and P.H. von Hippel. RNA displacement pathways during transcription from synthetic RNA-DNA bubble duplexes. Biochemistry, 33, 340-347 (1994).
173. Johnson, N.P., Lindstrom, J., Baase, W.E. and P.H. von Hippel. Double- stranded DNA templates can induce a-helical conformation in Ala/Lys- containing peptides: functional implications for bZip and bHLH transcription factors. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA., 91, 4840-4844 (1994).
174. von Hippel, P.H. Protein-DNA recognition: new perspectives and underlying themes. Science (Perspective), 263, 769-770 (1994).
175. von Hippel, P.H. Passing lanes for polymerases? Curr. Biol. (Dispatch), 4, 333- 336 (1994).
176. Wilson, K.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Stability of E. coli transcription complexes near an intrinsic terminator. J. Mol. Biol., 244, 36-51 (1994).
177. von Hippel, P.H., Fairfield, F.R. and M.K. Dolejsi. On the processivity of polymerases in "DNA Damage: Effects on DNA Structure and Protein Recognition" (S. S. Wallace, B. van Houten and Y. W. Kow, eds.). Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 726, 118-131, (1994).
178. Daube, S.S., Hart, C.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Coupling of RNA displacement and intrinsic termination during transcription from synthetic RNA-DNA bubble duplexes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 91. 9539-9548 (1994).
179. Reddy, M.K., Weitzel, S.E., Daube, S.S., Jarvis, T.C. and P.H. von Hippel. Using macromolecular crowding agents to identify weak interactions with DNA replication complexes. Methods in Enzymology, (J. Campbell, ed.), Academic Press, 262, 466-476 (1995).
180. von Hippel, P.H. A ring to bind eukaryotic DNA polymerase. Structure, 3, 123-124 (1995).
181. Dong, F., Gogol, E.P. and P.H. von Hippel. The phage T4-coded DNA replication helicase (gp41) forms a hexamer upon activation by nucleoside triphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7462-7473 (1995).
182. Wilson, K.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Transcription termination at intrinsic terminators: the role of the RNA hairpin. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 8793-8797 (1995).
183. Rippe, K., von Hippel, P.H. and J. Langowski. Action at a distance: DNA looping and initiation of transcription. Trends in Biochem. Sci. 20, 500-506 (1995).
184. Rees, W.A., Weitzel, S.E., Yager, T.D., Das, A. and P.H. von Hippel. Bacteriophage l N protein alone can induce transcription antitermination in vitro. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 342-346 (1996).
185. von Hippel, P.H., W,A, Rees, K. Rippe and K.S. Wilson. Specificity mechanisms in the control of transcription. Biophysical Chemistry (W.F. Harrington Memorial Issue), 59, 231-246 (1996).
186. Dong, F. and P.H. von Hippel. The ATP-activated helicase hexamer of bacteriophage T4 (gp41) forms a stable primosome on DNA with a monomer of T4-coded primase (gp61). J. Biol. Chem. 271, 19625-19631 (1996).
187. Das, A., Pal, M., Mena, J.G., Whalen, W., Wolska, K., Crossley, R., Rees, W., von Hippel, P.H., Constantino, N., Court, D., Mazzulla, M., Altieri, A.S., Byrd, R.A., Chattopadhyay, S., DeVito, J. and Ghosh, B. Components of multiprotein-RNA complex that controls transcription elongation in E. coli phage lambda. Methods in Enzymology, 274 374-402 (1996).
188. Latham, G.J., Pietroni, P., Dong, F., Young, M.C. and P.H. von Hippel. Fluorescence monitoring of T4 polymerase holoenzyme accessory protein interactions during loading of the sliding clamp onto the template•primer junction. J. Mol. Biol. 264, 426-439 (1996).
189. Young, M.C., Weitzel, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel.The kinetic mechanism of the formation of the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase sliding clamp. J. Mol. Biol. 264, 440-452 (1996).
190. Dong, F., Weitzel, S.E. and P.H. von Hippel. A coupled complex of T4 DNA replication helicase (gp41) and polymerase (gp43) can perform rapid and processive DNA strand-displacement synthesis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 14456-14461 (1996).
191. Van Gilst, M.R., Rees, W.A., Das, A. and P.H. von Hippel. Complexes of the N antitermination protein of phage l with specific and nonspecific RNA target sites on the nascent transcript. Biochemistry 36, 1514-1524 (1997).
192. Rippe, K., Guthhold, M., von Hippel, P.H. and C. Bustamante. Transcription activation via DNA-looping: vizualization of intermediates in the activation pathway of E. coli RNA polymerase s54 holoenzyme by scanning force microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 270, 125-138 (1997).
193. Walstrom, K.M., Dozono, J.M., Robic, S. and P.H. von Hippel. Kinetics of the RNA-DNA helicase activity of E. coli transcription termination factor rho. I. Characterization and analysis of the reaction. Biochemistry 36. 7980-7992 (1997).
194. Walstrom, K.M., Dozono, J.M. and P.H. von Hippel. Kinetics of the RNA-DNA helicase activity of E. coli transcription termination factor rho. II. Processivity, ATP consumption, and RNA binding. Biochemistry 36, 7993-8004 (1997).
195. Pontius, B.W., Lott, W.B. and P.H. von Hippel. Observations on catalysis by hammerhead ribozymes are consistent with a two-divalent-metal-ion mechanism. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2290-2294 (1997).
196. Rees, W.A., Weitzel, S.E., Das, A. and P.H. von Hippel. Regulation of the elongation-termination decision at intrinsic terminators by antitermination protein N of phage l. J. Mol. Biol. 273, 797-813 (1997).
197. Van Gilst, M.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Assembly of the N-dependent antitermination complex of phage l: NusA and RNA bind independently to different unfolded domains of the N protein. J. Mol. Biol. 274, 160-173 (1997).
198. Pietroni, P., Young, M.C., Latham, G.J. and P.H. von Hippel. Structural analyses of gp45 sliding clamp interactions during assembly of the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme. I. Conformational changes within the gp44/62-gp45-ATP complex during clamp loading. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 31666-31676 (1997).
199. Latham, G.J., Bacheller, D.J., Pietroni, P. and P.H. von Hippel. Structural analyses of gp45 sliding clamp interactions during assembly of the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme. II. The gp44/62 clamp loader interacts with a single defined face of the sliding clamp ring. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 31677-31684 (1997).
200. Latham, G.J., Bacheller, D.J., Pietroni, P. and P.H. von Hippel. Structural analyses of gp45 sliding clamp interactions during assembly of the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme. III. The gp43 DNA polymerase binds to the same face of the sliding clamp as the clamp loader. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 31685-31692 (1997).
201. von Hippel, P.H., Walstrom, K.M., Wilson, K.S. and A.Q. Zhu. Intrinsic and rho-dependent transcription termination in E. coli, in "Transcription: Modular Texts in Cell and Molecular Biology" (D.K. Hawley and M. Purton, eds.) Chapman & Hall, Publishers. London (in press).
202. Walstrom, K.M., Dozono, J.M. and P.H. von Hippel. Effects of reaction conditions on RNA secondary structure and on the helicase activity of Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. J. Mol. Biol. 279, 713-726 (1998).
203. Lott, W.B., Pontius, B.W. and P.H. von Hippel. A two metal ion mechanism operates in the hammerhead ribozyme-mediated cleavage of an RNA substrate. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 542-547 (1998).
204. Zhu, A.Q. and P.H. von Hippel. Mechanisms of rho-dependent transcript termination. I. Rho loading, template sequence, and kinetic competition with the trp t' terminator. Biochemistry 37, 11202-11214 (1998).
205. Zhu, A.Q. and P.H. von Hippel. Mechanisms of rho-dependent transcript termination. II. A quantitative model of rho-dependent transcript release. Biochemistry 37, 11215-11222 (1998).
207. Wilson, K.S., Conant, C.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Determinants of the stability of transcription elongation complexes: Interactions of the nascent RNA with the DNA template and the RNA polymerase. J. Mol. Biol., 289, 1179-1194 (1999).
208. Daube, S.S. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of the E. coli sigma70 within the transcription elongation complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scis., USA, 96, 8390-8395 (1999).
209. Alberts, B.M., Ayala, F.J., Botstein, D., Frank, E., Holmes, E.W., Lee, R.D., Macagno, E.R., Marrack, P., Oparil, S., Orkin, S.H., Rubenstein, A.H., Slayman, C.W., Sparling,, P.F., Squire, L.R., von Hippel, P.H. and K.R. Yamamoto. SCIENCE POLICY: Proposed Changes for NIH's Center for Scientific Review. Science, 285, 666-667 (1999).
210. Jing, D.H., Dong, F., Latham, G.J. and P.H. von Hippel. Interactions of bacteriophage T4-coded primase (gp61) with the T4 replication helicase (gp41) and DNA in primosome formation. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 27287-27298 (1999).
211. Latham, G.J., Dong, F., Pietroni, P., Dozono, J.M., Bacheller, D.J. and P.H. von Hippel. Opening of a Monomer-Monomer Interface of the Trimeric Bacteriophage T4-coded gp45 Sliding Clamp is Required for Clamp Loading onto DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scis., USA, 96, 12448-12453 (1999).
212. Van Gilst, M.R. and P.H. von Hippel. Quantitative dissection of a transcriptional control system: The N-dependent complex of phage l as a regulatory paradigm. Methods in Enzymology, Energetics of Biological Macromolecules, Part C, Michael L. Johnson and Gary K. Ackers, eds. 323, 1-31 (2000).
213. Pasman, Z. and P.H. von Hippel. NusG acts at the Escherichia coli transcription elongation complex to regulate rho-dependent transcript termination. Biochemistry 39, 5573-5585 (2000).
214. von Hippel, P.H. and Jing, D.H. Bit players in the trombone orchestra (Perspective). Science 287, 2435-2436 (2000).
215. von Hippel, P.H. The DNA Recombination-Replication Interface (Editorial) Trends in Biochemical Scis. 25, 155 (2000).
216. Delagoutte, E. and P.H. von Hippel. Molecular mechanisms of the functional coupling of the helicase (gp41) and DNA polymerase (gp43) of bacteriophage T4 within the DNA replication fork. Biochemistry 40 4459-4477 (2001)
217. von Hippel, P.H. and E. Delagoutte. A general model for nucleic acid helicases and their "coupling" within macromolecular machines. Cell 104, 177-190 (2001).
218. Pietroni, P., Young, M.C., Latham, G.J., and P.H. von Hippel. Dissection of the ATP-driven reaction cycle of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication processivity clamp loading system. J. Mol. Biol. 309, 869-891 (2001).
219. von Hippel, P.H. and Z. Pasman. Reaction pathways in transcript elongation. Biophys. Chem. (issue honoring John Schellman) (in press).
220. Pasman, Z. and P.H. von Hippel. Active E. coli transcription elongation complexes are functionally homogeneous. J. Mol. Biol. 322, 505- (2002).
221. Delagoutte, E. and P.H. von Hippel. Helicase mechanisms and the coupling of helicases within macromolecular machines. I. Structure and function of isolated helicases. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics 35, 431-478 (2002).
222. Delagoutte, E. and P.H. von Hippel. Helicase mechanisms and the coupling of helicases within macromolecular machines. II. Integration of helicases into cellular processes. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics 36, 1-69 (2003).
223. Delagoutte, E. and P.H. von Hippel. Function and assembly of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication complex: Interactions of the T4 polymerase with various model DNA constructs. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 25435-25447 (2003).
224. von Hippel, P.H. and E. Delagoutte. Macromolecular complexes that unwind nucleic acids. BioEssays, 25, 1168-1177 (2003).
225. von Hippel, P.H. Graduate days at M.I.T. Biophys. Chem. (Special Issue Honoring David Yphantis). 108, 17-22 (2004).
226. Johnson, N.P., Baase, W.A. and P.H. von Hippel. Low energy circular dichroism of 2-aminopurine dinucleotide as a probe of local conformation of DNA and RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scis., USA, 101, 3426-3431 (2004).
227. von Hippel, P.H. Helicases become mechanistically simpler and functionally more complex. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 11, 494-496 (2004).
228. von Hippel, P.H. Completing the view of transcriptional regulation. Science, 305, 350-352 (2004).
229. Greive, S.J. and P.H. von Hippel. Thinking quantitatively about transcription regulation. Nature Reviews: Molecular and Structural Biology 6, 221-232 (2005)
230. Delagoutte, E. and P.H. von Hippel. Mechanistic studies of the T4 DNA (gp41) replication helicase: Functional interactions of the C-terminal tails of the helicase subunits with the T4 (gp59) helicase loader protein. J. Mol. Biol. 347. 257-275 (2005).
231. Conant, C.R., Van Gilst, M.R., Weitzel, S.E., Rees, W.A. and P.H. von Hippel. A quantitative decription of the binding states and in vitro function of antitermination protein N of bacteriophage l. J. Mol. Biol. 348, 1039-1059 (2005).
232. Johnson, N.P., Baase, W.A. and P.H. von Hippel. Investigating local conformations of double-stranded DNA by low energy circular dichroism of pyrrolo-cytosine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scis., USA 102, 7169-7173 (2005).
233. Johnson, N.P., Baase, W.A. and P.H. von Hippel. Low energy CD of RNA hairpin unveils a loop conformation required for _N-antitermination activity. J. Biol. Chem. (being revised).